Random News on Battling COVID-19 After Infection
I do my best to keep up with the news by watching MSNBC-- I have many reasons for watching it rather than CNN or FOX-News. However my primary reason: I agree with much of what I hear. CNN is good source. However, FOX-News seems to dumb-down its viewers. Anyhow, a couple of weeks ago I was listening to Rachel Maddow at her appointed time of 9pm EDT. She said something quite plain but profound-- there are other ways to treat COVID-19 infections. Prevention through vaccination may not be the only route. It struck me as strange-- so many unlucky souls have passed on but there are a lucky few who have been given "mystery" treatments after infection. The former president (#45) happened to be one of them.
While I am unsure what the treatment cocktail consisted for the former president, I ran across an interesting post at the American Chemical Society-- an antibacterial that seems to be effective against COVID-19 (a virus). Anti-bacterials are normally ineffective against viruses. Ask your Family Physician why they are reluctant to prescribe penicillin for a cold (that is viral in nature)--- it can cause a secondary illness. Anti-bacterials have compounded the simple colds in many patients who have viral infections.
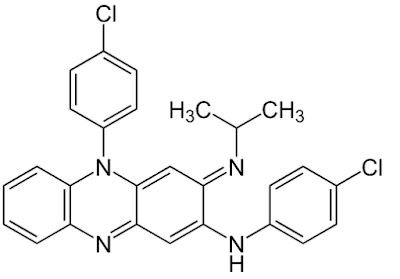
Seeing this molecule definitely piqued my interest. So, lets try to unpack it, bit-by-bit.
The molecule in question is known by its common (chemical) name -- Clofazimine. It is a molecule that is also apart of the "dye family" -- you read that correctly. The molecule is a dye, and it also functions as an antibacterial. It is primarily effective against the Tuberculosis bacterium and used in the fight against leprosy.
In all its 2-dimensional glory:
This so-called mystery molecule is used in conjunction with certain Anti-viral drugs to inhibit the effects of infection. You can find more information at the following website address: Clofazimine broadly inhibits coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2 (nature.com). Molecules like Clofazimine function by scissoring DNA molecules and therefore making it more difficult for the virus to replicate in the host.
It is a rather startling find-- this molecule is most likely a carcinogen, as well. It is a carcinogen for the same reason because it scissors viral DNA molecules. (The process is also known to produce Free-Radicals, as well-- another bad side effect).
However, use of this molecule to combat COVID is fantastic news-- It will most likely undergo trials with anti-viral compounds to beat COVID infections. The treatment regimens may be fairly inexpensive because this molecule is in formularies throughout the world.
Comments
Post a Comment